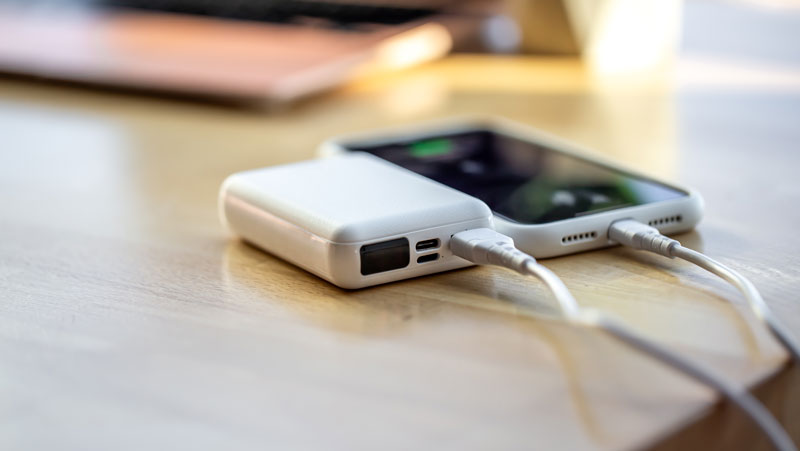
The topic of powerbanks on planes has been in the news again recently. As a Virgin Atlantic flight has made an emergency landing in Boston after a fire broke out on board.
Police believe a mobile phone power bank may have caused the fire as a device was found between the cushions of the seat where the blaze started.
No major injuries were reported, and all 217 passengers were safely evacuated from the aircraft at Boston’s Logan International Airport. Click here to find out more.
It is not the first instance where a portable charger was thought to be the cause of a plane fire.
Why are power banks prohibited in the cargo hold on flights?
Airlines do not allow power banks in the cargo luggage for the purpose of safety. Power banks are essentially batteries that utilize lithium cells. As lithium batteries are more likely to combust and are therefore prohibited for cargo transport, as part of air-transport regulations.
So, you don’t want them in the baggage compartment. If they’re taken on board as hand baggage, in the rare situation that they may catch fire, they can be dealt with more easily as there are fire extinguishers in the cabin.
What kind of power banks are allowed on planes?
The following rules are according to the Civil Aviation Administration in China. These rules are standard for many airlines around the world:
- Power bank must be carried for personal use.
- Power bank must only be carried in hand luggage or carried around. It is not allowed to carry power banks in checked luggage.
- If the rated power is less than 100Wh, power banks can be carried without approval; power banks with the power between 100Wh and 160Wh can be carried after the approval of the air carrier. However, each passenger is only allowed to carry no more than two power banks.
- It is not allowed to carry the power banks with power higher than 160Wh or the power banks without identified rated power and with rated power unable to be worked out with the marked parameters. Attachment: Calculation methods for the rated power of power banks.”
How Is Wh Calculated?
Here is the method to find Watt Hours: Just take Milliamp Hours/1000 x Voltage = Watt Hours (mAh)/1000 x (V) = (Wh)
For example, our Powerbank Plus which has an 8000 mAh and an output voltage of 40 =
8000 mAh / 1000 = (8 x 5V) 40 Watt Hours
Does My Power Bank Need Any Protections to Fly With?
The number of protections found in power banks depends on who produced it. A RAVPower power bank typically features these common protections:
- Over Current Protection: Stops the power bank from delivering a current that exceeds the amplitude of the connected device. Safety mechanisms like circuit breakers, overcurrent relays, and fuses provide instantaneous protection.
- Over Charge Protection: Prevents the power bank from continuing to charge a device that is outside the protection range (3.00 V to 4.20 V). This will avoid thermal runaway.
- Short Circuit Protection: This is another type of overcurrent protection. In this situation, the protection ensures that there is always a direct path for the current to travel. This prevents the cell from overheating which can cause a fire.
- Over-Discharge Protection: Stops the discharge rate from falling below 2.7 V/cell to 3.00 V/cell. This reduces battery cell stress and allows some extra power to self-discharge down to 2.50 V/cell. When that happens, the lithium-ion battery will “sleep” to protect against itself.
- High-Temperature Protection: Prevents the power bank from charging or discharging when battery temperature exceeds 60°/140F*.
Our Powerbanks (PB01, PB119 and PB116) have passed allitridum simulation, thermal, vibration, shock, external short circuit impact and forced discharge tests, which meet the United Nations “recommendations on the transport of dangerous goods” manual of Tests and Criteria (ST/SG/AC.10/11/Rev.6), Part 111 sub-section.
To order your Personalised Powerbank today please click here!